

Product Details
| Product Name | Dihexylamine |
| Alias | Bis(1-hexyl)amine; di-Normal-hexylamine; N,N-Dihexylamine; N-Hexyl-1-hexanamine; N-Hexylhexanamine |
| English | |
| Molecular formula | C12H27N |
| Molecular weight | 185.35 |
| CAS No | 143-16-8 |
| EINECS | |
| Specification | Assay(GC)98% |
| Appearance traits | |
| Use | For solvent, pharmaceutical industry, organic synthesis intermediates. |
| Package | 160kg/drum |
| Other product information | Properties: Appearance:Colourless liquid, Melting point:3 °C Boiling point:193.5°C Density:0.795 g/ml at 25 °C Vapor density:6.4 (vs air) Refractive index:N20/D 1.432 Flash(ing) point:203 °F Water soluble properties:Miscible with water. |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
DI-N-HEXYLAMINE may be sensitive to prolonged exposure to air. Insoluble in water. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
DI-N-HEXYLAMINE neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions to form salts plus water. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen may be generated in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides. |
|
Health Hazard |
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: DI-N-HEXYLAMINE is readily absorbed through the skin. |
|
Fire Hazard |
DI-N-HEXYLAMINE is combustible. |
|
Safety Profile |
poison by ingestion, skin contact, and intravenous routes. A skin exposed to heat or flame; can react with oxidizing materials. To fight fire, use CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also AMINES. |
|
General Description |
Clear colorless liquid. |
InChI:InChI=1/C12H27N/c1-3-5-7-9-11-13-12-10-8-6-4-2/h13H,3-12H2,1-2H3/p+1
Since its inception, the company has continuously expanded its business varieties and fields, to realize the business pattern with the expansion upstream and downstream as well as the complementary of internal and foreign trade. Based on technological innovation and guided by market orientation, we will accelerate the main business strategy, optimize supply chain elements, and build business flow, logistics flow, information flow, and capital flow in one mode, laying a solid foundation for supplying more high-quality and efficient services to a wider range of customers.
Hydroaminomethylation of terminal as wel...
We herein describe an efficient, CO2-tun...
Flow reaction methods have been develope...
In the present study, ruthenium-catalyze...
The reductive amination of carboxylic ac...

hexan-1-amine
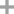

Dipentylimine

1-Pentyl-1-hexylamine


dihexylamine


Di-n-amylamine
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With hydrogen; nickel; In cyclohexane; at 90 ℃; under 12000.9 Torr; Product distribution; Kinetics; Mechanism;
|

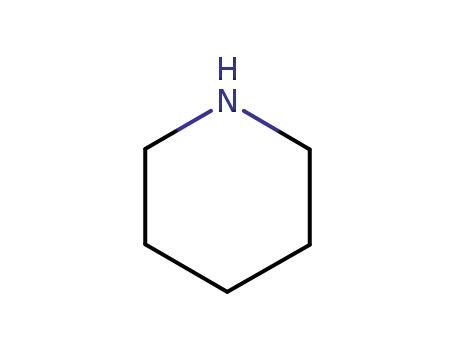
1-hexylpiperidine

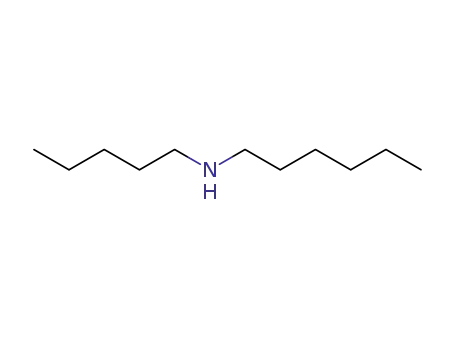
piperidine

1-pentylpiperidine


1-Pentyl-1-hexylamine


dihexylamine


Di-n-amylamine

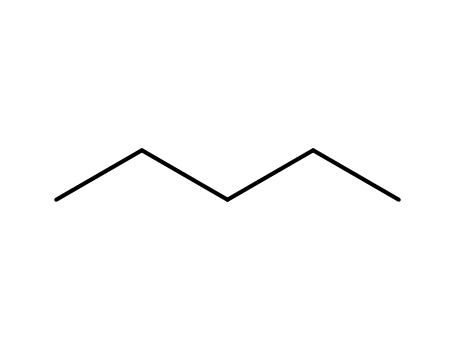
pentane
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With hydrogen; sulphidized CoO-MoO3; at 300 ℃; for 8h; under 45003.6 - 90757.2 Torr; Mechanism; Product distribution;
|
5.8% 5.4% 3% 0.8% |
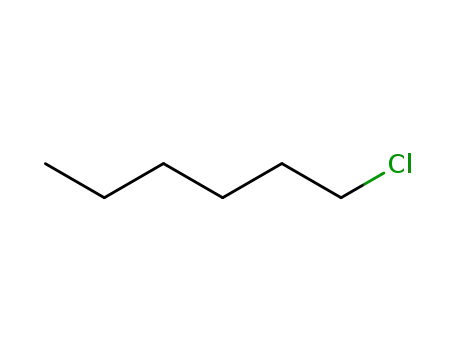
1-Chlorohexane

hexan-1-amine
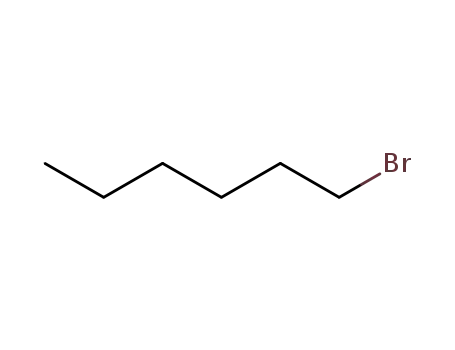
1-bromo-hexane

N,N-di(hexyl)benzylamine
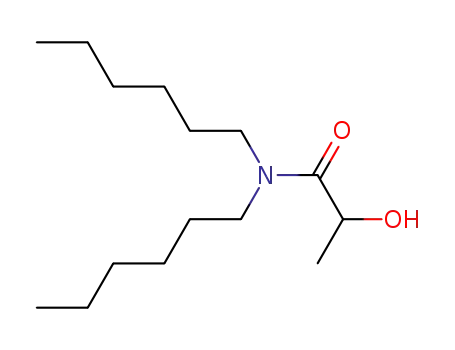
N,N-dihexyl-lactamide

1-(2-chloro-phenoxy)-3-dihexylamino-propan-2-ol
hexanenitrile

tri-n-hexylamine
CAS:80-70-6
CAS:10061-68-4
CAS:2212-32-0