Your Location:Home >Products >Inorganic chemicals >Rare light metals(Li,Rb,Cs,Be) >Lithium(Li) >10377-51-2
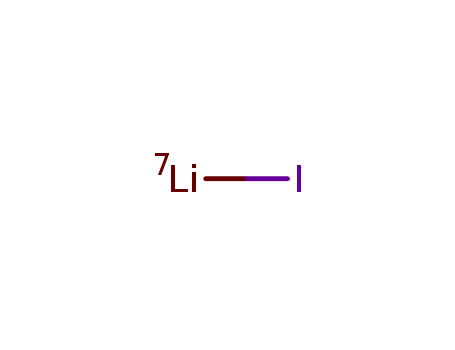
Product Details
| Product Name | Lithium iodide | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alias | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| English | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | LiI |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular weight | 133.85 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS No | 10377-51-2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EINECS | 233-822-5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Specification | 99% 99.9% |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance traits | White crystal. Deliquescence. In case of light or a long time, the color becomes yellow. Soluble in water, alcohol and acetone, ethyl ether. When melting, it will erode the glass and ceramics; Moisture proof seal |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Use | For the pharmaceutical industry, photographic industry and synthetic related synthetic crystals. Lithium battery manufacturing raw materials |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Package | 2KG/ plastic bottle |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other product information |
|
|
General Description |
Lithium iodide is an ionic compound composed of lithium ions (Li⁺) and iodide ions (I⁻). It crystallizes in the NaCl structure and can form hydrates under certain conditions. |
| Uses | Used in molten salt batteries for its stability and conductivity. Lithium iodide enhances ion transport and stabilizes electrode interfaces. Lithium iodide has demonstrated remarkable potential in stabilizing lithium-metal anodes. By forming a uniform SEI layer through reactions with iodine vapor, it effectively mitigates dendrite growth and extends battery life. These improvements address major safety and efficiency challenges in high-energy battery systems like Li-S and Li-O₂ batteries. |
| Combustible and Toxic | Lithium iodide can cause irritation to the eyes, skin, and respiratory tract. Prolonged exposure may result in abdominal pain and kidney damage. |
InChI:InChI=1/HI.Li/h1H;/q;+1/p-1
Hangzhou Ocean chemical Co.,Ltd.is a chemical supplier that provides stable product quality, unique technical support and high quality service for global customers, Headquarters is located at Hangzhou with superior entrepreneurial environment and business climate.
It has been revealed that the anion additive, lithium iodide (LiI), can tune the cell chemistry to form lithium hydroxide (LiOH) as the product and facilitate the kinetics during the charging process. Although numerous studies have been reported, the role of this additive is still under investigation.
The metallic lithium (Li) is the ultimate option in the development of anodes for high-energy secondary batteries. Unfortunately, inferior cycling reversibility and Li dendrites growth of Li metal as anode enormously impede its commercialization.
Here, the interface between lithium thiophosphate and lithium iodide-doped lithium thiophosphate with lithium metal is investigated. Lithium iodide plays a protective role at the interface and enables improved lithium cycling. Operando transmission electron microscopy analysis reveals delamination and dead lithium at the interface as major challenges for solid-state batteries.
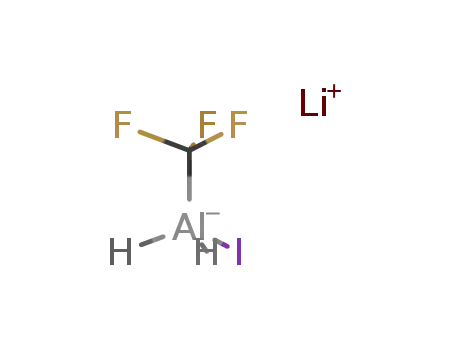
lithium (trifluoro methyl) iodo aluminate

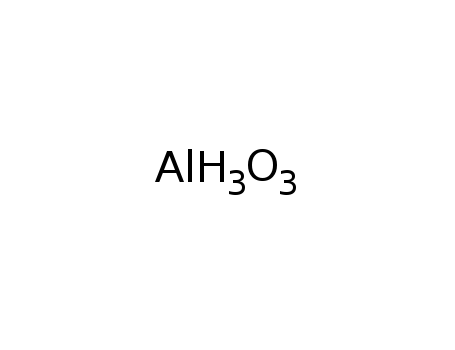
aluminum trihydroxide
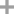
aluminum(III) fluoride

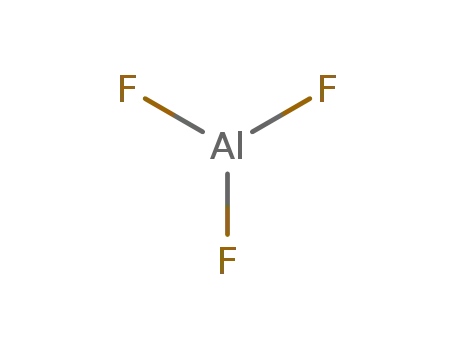
methane

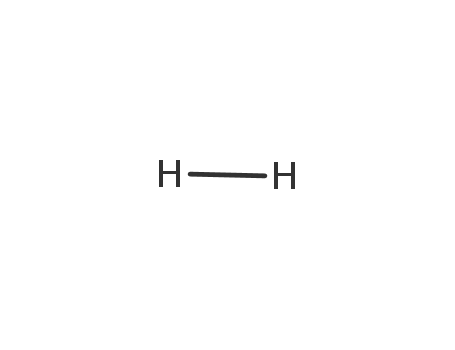
hydrogen

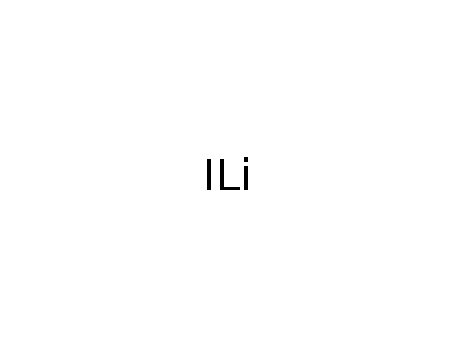
lithium iodide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With water; In water; decomposition with water;;
|
Li(1+)*[AuI4](1-)=Li[AuI4]

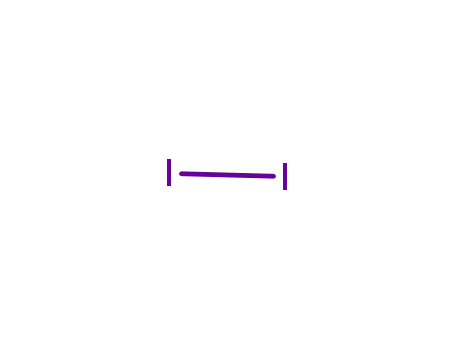
iodine


gold

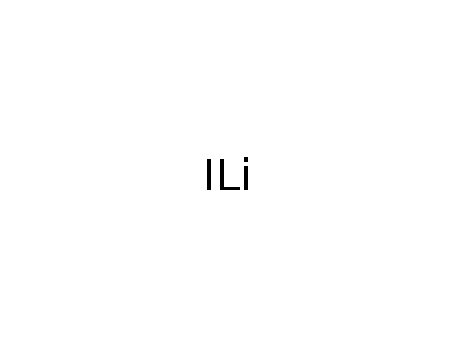
lithium iodide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In neat (no solvent); 20°C, air atm.;
|

iodine

lithium
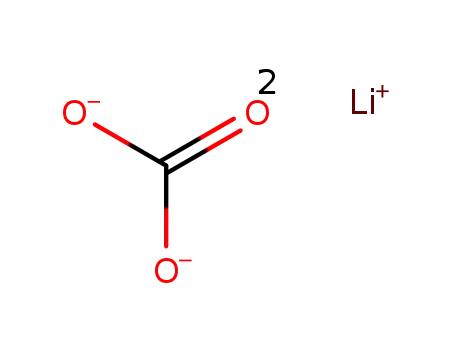
lithium carbonate

lithium aluminium tetrahydride
triiodide(1-)

sulfur
dicarbonylcyclopentadienyliodoiron(II)
tris(triphenylphosphine)rhodium(I) iodide
CAS:12027-06-4
CAS:7789-17-5
CAS:80-70-6
CAS:10061-68-4