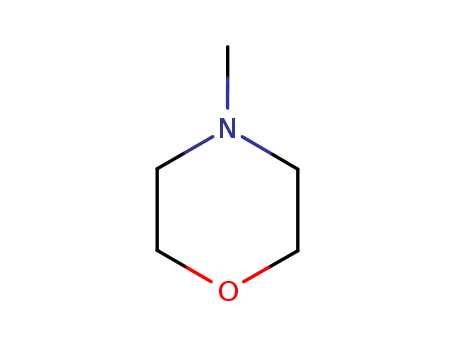

Product Details
| Product Name | N-Methylmorpholine |
| Alias | 1-Methylmorpholine ;4-Methylmorpholine;Morpholine,N-methyl |
| English | |
| Molecular formula | C5H11NO |
| Molecular weight | 101.15 |
| CAS No | 109-02-4 |
| EINECS | |
| Specification | Assay(GC)99% Water :<0.3%; Color :<100#(APHA) |
| Appearance traits | Colorless liquid, with the smell of ammonia |
| Use | Medium of pharmaceuticals and chemical synthesis of organic synthetic raw material, the analytical reagent, extraction solvent, chlorine hydrocarbon stabilizer, corrosion inhibitor and dispersant, catalyst, medicine production, etc |
| Package | 180kg/drum |
| Other product information | Properties: Melting point:−66°C(lit.) Boiling point:115-116°C750 mm hg(lit.) Density:0.92 g/ml at 25°C(lit.) Vapor density:>1 (vs air) Vapour pressure:18 mm hg ( 20°C) Refractive index:N20/D 1.435(lit.) Flash(ing) point:75 °F Water soluble properties:>500 g/L (20ºc) |
|
Preparation |
4-Methylmorpholine preparation method is to slowly add formaldehyde in morpholine drop by drop, under stirring add formic acid reaction, automatic reflux, and release carbon dioxide. After adding formic acid, heating reflux 4 ~ 5h, cooling and adding sodium hydroxide immediately distillation, collect all the fraction before the boiling point of 99 ℃, and then add sodium hydroxide in the fraction to saturation, cooling the oil layer, drying, fractional distillation, to obtain N-methylmorpholine. |
|
Synthesis Reference(s) |
Tetrahedron Letters, 36, p. 4881, 1995 DOI: 10.1016/0040-4039(95)00875-D |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Highly flammable. Insoluble in water. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Amines are chemical bases. They neutralize acids to form salts plus water. These acid-base reactions are exothermic. The amount of heat that is evolved per mole of amine in a neutralization is largely independent of the strength of the amine as a base. Amines may be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is generated by amines in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides. |
|
Hazard |
Flammable, dangerous fire risk. Skin irri-tant. |
|
Health Hazard |
May cause toxic effects if inhaled or ingested/swallowed. Contact with substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Vapors may cause dizziness or suffocation. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Flammable/combustible material. May be ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated. Many liquids are lighter than water. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Flammable |
|
Safety Profile |
Moderately toxic by ingestion and skin contact. Mildly toxic by inhalation. An irritant to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Flammable when exposed to heat or flame, can react vigorously with oxidizing materials. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. |
|
Purification Methods |
Dry it by refluxing with BaO or sodium, then fractionally distil it through a helices-packed column. The picrate has m 227o, the thiocyanate salt has m 103o (from butanone). [Hall J Phys Chem 60 63 1956, Beilstein 27 I 203, 27 III/IV 22.] |
|
General Description |
A water-white liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Less dense than water and insoluble in water. Flash point 75°F. May be moderately toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. Very irritating to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Used as a solvent and to make pharmaceuticals. |
InChI:InChI=1/C5H11NO/c1-6-2-4-7-5-3-6/h2-5H2,1H3/p+1
Our main markets are China, the United States, Europe, Korea, and Japan. The main business scope includes electronic chemicals, liquid crystal intermediates, high-purity metal compounds, pharmaceutical intermediates, special chemicals, and so on.
-
The synthesis of N-methylmorpholine from...
Prochiral aminoketones are key intermedi...
The first acceptor-free heavier germaniu...
-
In new biorefinery processes, NMMO/water...
The two carbon-centered radicals 4-morph...
Reaction of chiral phosphorodiamidites w...
The reduction of CO2 with amines and H2 ...
An improved mild and selective method fo...
-
The catalytic networks of methylotrophic...
Bis-NHC stabilized germyliumylidenes [RG...
Reaction of nitrones and N-oxides with b...
(Chemical Equation Presented) A kinetic ...
Formic acid is used as the sole carbon a...
[Figure not available: see fulltext.] Al...
Herein, we disclose that electrochemical...
We report herein that a borane-trimethyl...
C19H22(2)H2NO(1+)

4-methyl-morpholine

trans-1,2-dideuteriostilbene
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With N,N'-bis-(4-ethoxy-phenyl)-thiourea; In ethanol; at 40 ℃; Rate constant;
|
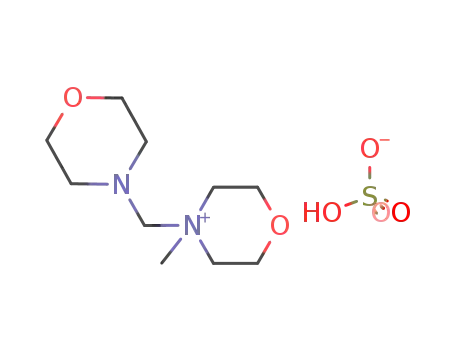
4-methyl-4-(morpholinomethyl)morpholinium sulfate

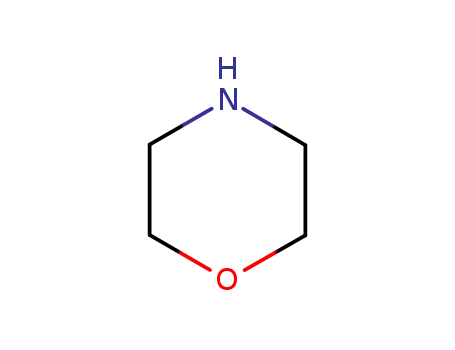
morpholine


4-methyl-morpholine

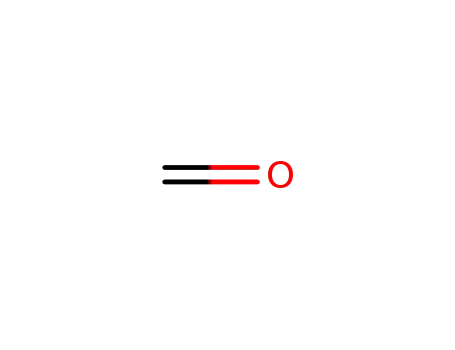
formaldehyd
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In water; Product distribution;
|

morpholine
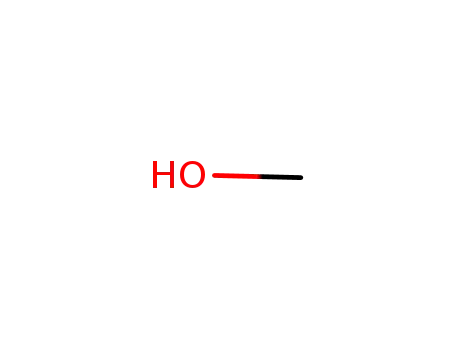
methanol
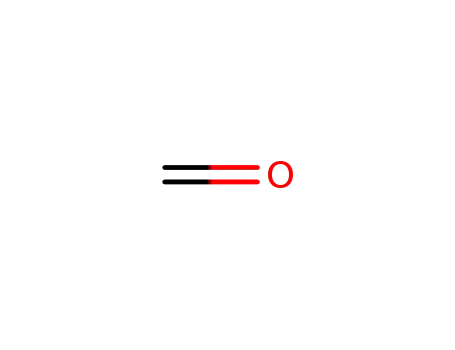
formaldehyd
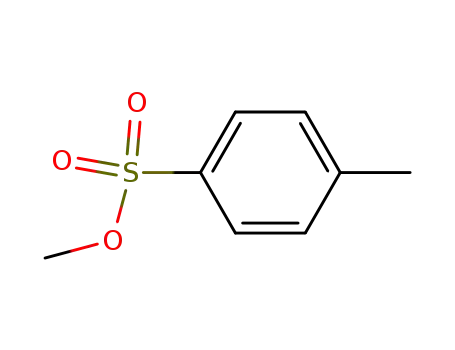
methyl p-toluene sulfonate
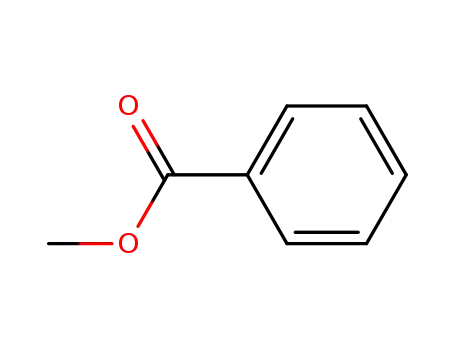
benzoic acid methyl ester
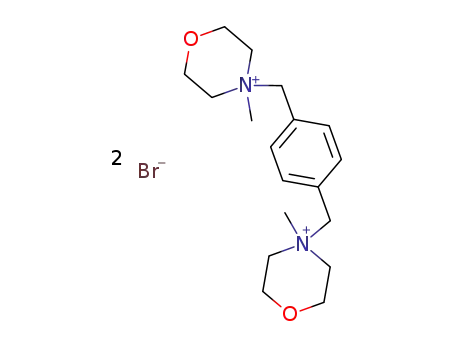
4,4'-dimethyl-4,4'-p-xylylene-bis-morpholinium; dibromide
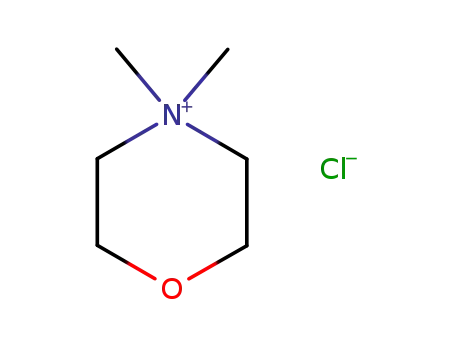
4,4-dimethylmorpholinium chloride
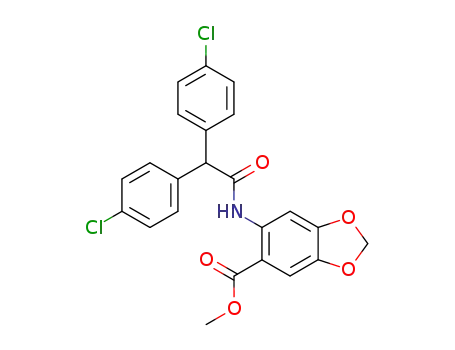
6-[2,2-bis-(4-chloro-phenyl)-acetylamino]-benzo[1,3]dioxole-5-carboxylic acid methyl ester
CAS:123-00-2
CAS:1704-62-7
CAS:103-76-4
CAS:12008-21-8