Your Location:Home >10026-06-9

Product Details
| Product Name | Tin (V) Chloride Pentahydrate |
| Alias | tin(iv) tetrachloride pentahydrate |
| English | |
| Molecular formula | Cl4H10O5Sn |
| Molecular weight | 350.6 |
| CAS No | 10026-06-9 |
| EINECS | 231-588-9 |
| Specification | analysis reagent grade( AR grade) Appearance White crystal Test of Clarity Pass Assay 99.50% min As :0.0005% max Fe: 0.001% max Sb:0.005% max SO4: 0.005% max Substances not precipitated by hydrogen sulfide :0.05% max |
| Appearance traits | Properties:White to yellow solid. Melting point: 56 ° C; Boiling point: 14.1 ° C at 760 mmHg |
| Use | Used as analytical reagent, organic synthesis dewatering agent and mordant |
| Package | 25KG/ drum |
| Other product information |
|
Preparation |
Tin(IV) chloride is prepared by reacting tin or tin(II) chloride with chlorine: Sn + 2Cl2 → SnCl4 SnCl2 + Cl2 → SnCl4 |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Soluble in water. Reacts with water to form Hydrochloric Acid in dense white fumes [Merck 11th ed. 1989]. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
Acidic salts, such as STANNIC CHLORIDE, are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydrogen ions and have pH's of less than 7.0. They react as acids to neutralize bases. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of inorganic acids, inorganic oxoacids, and carboxylic acid. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible. Many of these compounds catalyze organic reactions. |
|
Hazard |
Toxic material |
|
Health Hazard |
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. |
|
Safety Profile |
A poison by intraperitoneal and intravenous routes. Mutation data reported. A corrosive liquid. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of tin and Cl-. |
|
Potential Exposure |
Hydrated stannic chloride is used for fixing certain textile dyes, and for treating silk to give weight to the fabric. |
|
Shipping |
UN2440 Stannic chloride, pentahydrate, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material. |
|
Incompatibilities |
Reacts violently with water, forming corrosive hydrochloric acid and tin oxide fumes. Reacts with turpentine, alcohols, and amines, causing fire and explosion hazard. Attacks many metals; some forms of plastics, rubber, and coatings. Reacts with moist air to form hydrochloric acid and dense white fume. |
|
Physical Properties |
Colorless fuming liquid; corrosive; density 2.234 g/mL; freezes at –33°C; boils at 114.15°C; critical temperature 318.75°C; critical pressure 37.98 atm; critical volume 351 cm3/mol; soluble in cold water, evolving heat; decomposed by hot water; soluble in alcohol, benzene, toluene, chloroform, acetone and kerosene. The pentahydrate is a yellowish-white crystalline solid or small, fused lumps; faint odor of HCl; density 2.04 g/cm3; decmposes at 56°C; very soluble in water; soluble in ethanol. |
|
General Description |
Stannic chloride pentahydrate is a white colored solid. Stannic chloride pentahydrate is soluble in water. Stannic chloride pentahydrate is toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. Stannic chloride pentahydrate is used to make perfumes and dyes. |
InChI:InChI=1/4ClH.5H2O.Sn/h4*1H;5*1H2;/q;;;;;;;;;+4/p-4
High-quality chemical talents, abundant product resources, a perfect supply chain, a reasonable organizational structure, and a scientific management model are the core competitiveness of our company's continuous development. Based on good credibility, cooperation, development, and win-win purpose, after years of efforts, the company has established stable cooperative relationships with more than hundreds of chemical enterprises in domestic and established a good reputation and corporate image in the chemical field.
The solid state redox reaction of iron (...
Several mixtures of compounds 1 and 2 we...
tin(II) chloride dihdyrate
iron(III) oxalate pentahydrate

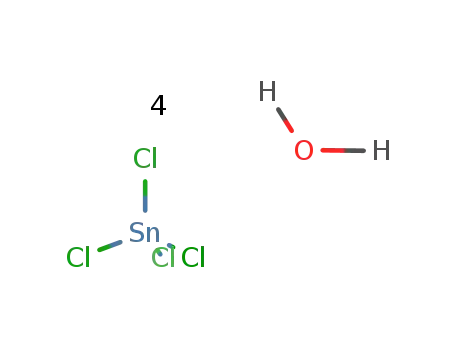
tin(IV) chloride tetrahydrate

Sn(2+)*C2O4(2-)*3H2O=SnC2O4*3H2O

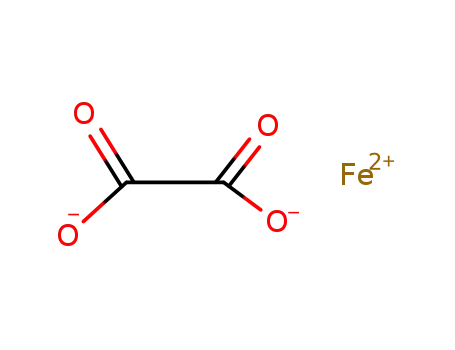
FeC2O4, α
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
In neat (no solvent, solid phase); Solid state reaction in hydrogen or helium atmosphere.; Gas chromatography, Moessbauer spectroscopy.;
|
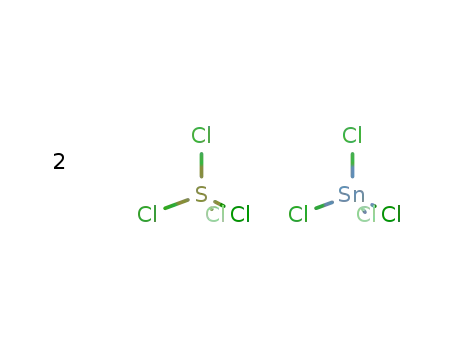
tin(IV) chloride * 2 sulfur tetrachloride

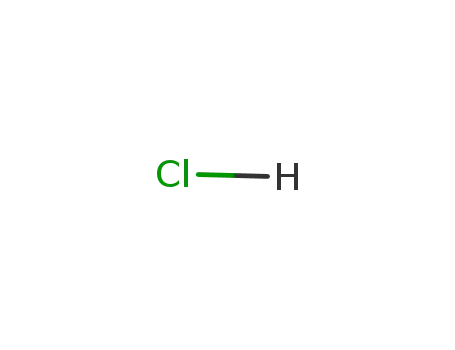
hydrogenchloride

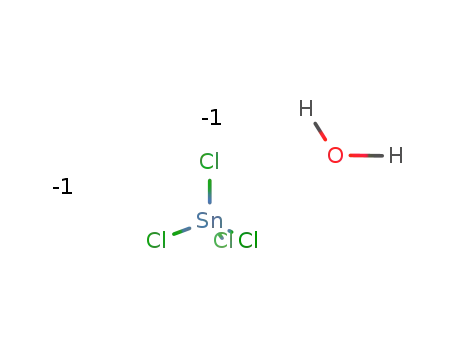
tin(IV) chloride hydrate

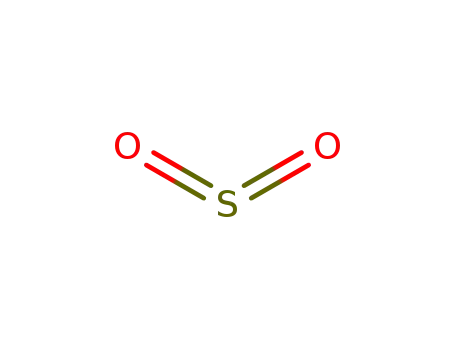
sulfur dioxide
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With air; In neat (no solvent); fuming in air with decompn.;;
|
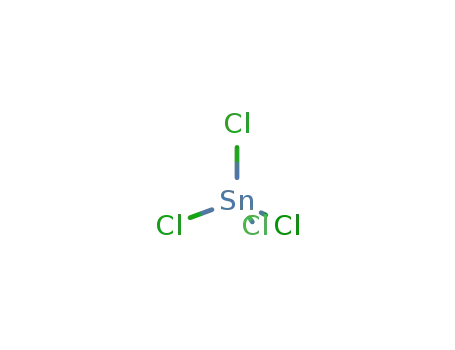
tin(IV) chloride
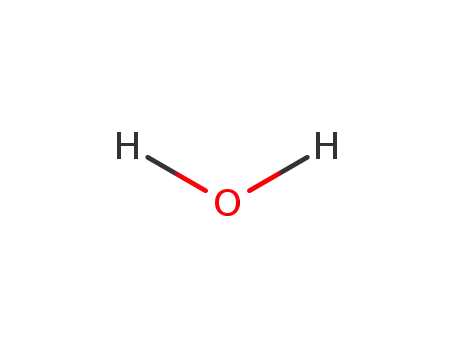
water
chlorine

hydrogenchloride
bis(toluene-3,4-dithiolato)tin(IV)
CAS:7646-78-8
CAS:1314-95-0
CAS:2444-36-2
CAS:4418-61-5