Your Location:Home >Products >Organic Chemicals >Biological buffer >5625-37-6

Product Details
| Product Name | PIPES |
| Alias | |
| English | PIPES |
| Molecular formula | |
| Molecular weight | |
| CAS No | 5625-37-6 |
| EINECS | |
| Specification | 99% |
| Appearance traits | white powder |
| Use | |
| Package | 25kg/drum |
| Other product information |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Notclassified |
|
Purification Methods |
Purify PIPES from boiling water (maximum solubility is about 1g/L) or as described for ADA [N-(2-acetamido)iminodiacetic acid above]. [Good et al. Biochemistry 5 469 1966, Beilstein 23/12 V 380.] |
|
description |
PIPES free acid, also known as 1,4-piperazinediethanesulfonic acid, is a Good's buffer notable for having a pKa value similar to ordinary physiological pH. As such, PIPES free acid is frequently used as a buffer in biochemical research.PIPES is a zwitterionic, piperazinic buffer that is useful for a pH range of 6.1 – 7.5. PIPES lacks the ability to form a significant complex with most metal ions and is recommended for use as a non-coordinating buffer in solutions with metal ions. PIPES has wide variety of applications and is commonly used in cell culture media, in protein crystallization, as a running buffer in gel electrophoresis, and as an eluent in isoelectric focusing and chromatography. This buffer is capable of forming radicals and is therefore not suitable for redox reactions. It is suitable for use in the bicinchoninic acid (BCA) assay. Solubility of PIPES increases when the free acid is converted to the sodium salt.Buffers are made by adding base solution to PIPES free acid and titrating to the desired pH. |
|
Application |
Glutaraldehyde fixation of plant and animal tissue samples can cause loss of lipid, leading to apparent morphological changes. Lipid loss and artifacts were minimized when PIPES was used to buffer the glutaraldehyde fixative.Alkaline phosphatase activity is lost selectively from certain rat hepatocyte organelles when fixed for ultracytochemistry with cacodylate-buffered glutaraldehyde. When PIPES was used as buffer, retention of activity was 60% greater.Fixation of fungal zoospores for fluorescence microscopy and electron microscopy was optimal with a combination of glutaraldehyde and formaldehyde in PIPES buffer. |
|
General Description |
PIPES is a member of the ethanesulfonic acid buffer series, first introduced by Good et al., developed to meet certain criteria: midrange pKa, maximum water solubility and minimum solubility in all other solvents, minimal salt effects, minimal change in pKa with temperature, chemically and enzymatically stable, minimal absorption in visible or UV spectral range and easily synthesized. Since its pKa at 37 °C is near physiological pH, PIPES has applications in cell culture work. |
InChI:InChI=1/C8H18N2O6S2/c11-17(12,13)7-5-9-1-2-10(4-3-9)6-8-18(14,15)16/h1-8H2,(H,11,12,13)(H,14,15,16)
Our main markets are China, the United States, Europe, Korea, and Japan. The main business scope includes electronic chemicals, liquid crystal intermediates, high-purity metal compounds, pharmaceutical intermediates, special chemicals, and so on.
The reaction is carried out in such a ma...
The present invention relates to a metho...
-
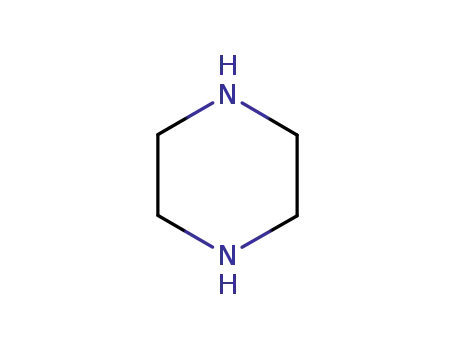
piperazine
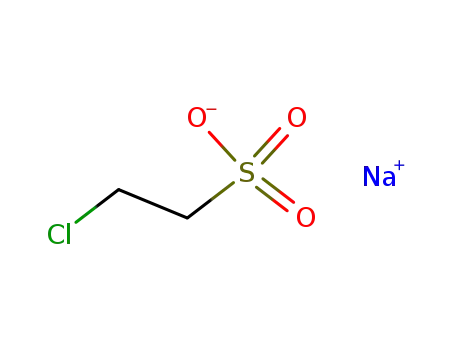
Na-salt of 2-chloroethane-1-sulfonic acid

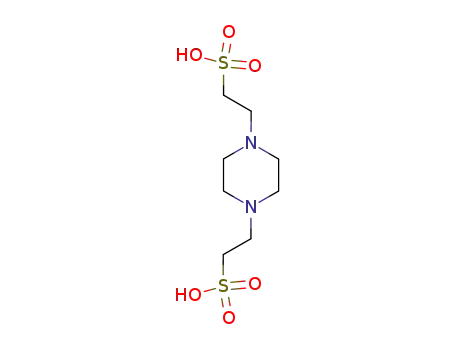
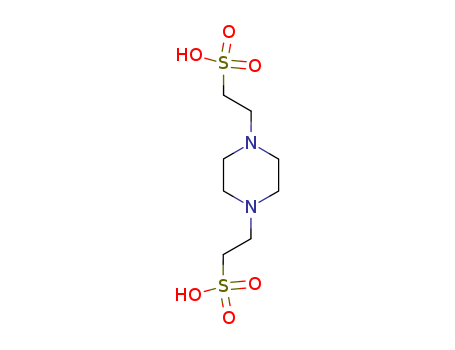
2,2'-piperazine-1,4-diyl-bis-ethanesulfonic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With sodium hydroxide; In water; for 3h; pH=9 - 9.5;
|
86.3% |


2,2'-piperazine-1,4-diyl-bis-ethanesulfonic acid
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
Natriumbromaethansulfonat, Piperazin*6H2O;
|
|
|
|

piperazine

Na-salt of 2-chloroethane-1-sulfonic acid
CAS:7365-82-4
CAS:10191-18-1
CAS:10026-12-7
CAS:29915-38-6